Architecting Headless E-commerce for Generative Discovery with Vercel and Builder.io
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) for Headless Stacks?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) for headless architectures requires transitioning from Client-Side Rendering to Server-Side Rendering (SSR) on Vercel to ensure AI crawler legibility. By structuring content as semantic entities in Builder.io and injecting dynamic JSON-LD schema, developers transform static pages into reasoning-ready data sources that Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Perplexity can synthesize and cite
At Seeed.us, we engineer digital platforms that bridge the gap between CMO goals and CTO execution. We see a fundamental shift in how visibility works: the transition from "blue links" to "synthesized answers." Traditional SEO optimizes for retrieval; GEO optimizes for reasoning.
If you run a headless stack using Next.js, Vercel, and Builder.io, you possess a distinct advantage in this new landscape, but only if you re-architect your rendering and data delivery strategies immediately.
Why does Client-Side Rendering fail AI crawlers?
Client-Side Rendering (CSR) acts as a failure mode for Generative AI visibility. While Googlebot executes JavaScript relatively well, AI crawlers like GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot prioritize speed and cost-efficiency. They often do not execute the client-side JavaScript required to hydrate a CSR page, meaning they see an empty HTML shell rather than your product data.
To secure visibility in AI-generated answers, you must serve fully rendered HTML in the initial payload. We utilize Vercel’s infrastructure to deploy Next.js applications using Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR). This ensures that when an AI agent requests a URL, it receives the full text, pricing, and specs immediately, without waiting for hydration.
Technical Insight: "If the content is not present in the initial HTML payload, it is essentially non-existent to the generative engine." — Luis Martines, Head of Dev at Seeed.us.
How should we configure Robots.txt for Agentic Commerce?
You cannot optimize for AI if you block the agents trying to find you. Many engineering teams aggressively block AI bots to prevent data scraping, but this inadvertently destroys visibility in SearchGPT and Perplexity.
We configure Vercel deployments with a nuanced robots.txt that distinguishes between training bots and search retrieval bots. You must explicitly allow agents that drive real-time traffic.
Recommended Configuration:
User-agent: GPTBot Allow: / # Enables training presence User-agent: OAI-SearchBot Allow: / # Critical for visibility in real-time ChatGPT search User-agent: PerplexityBot Allow: / # Essential for Perplexity's answer engine
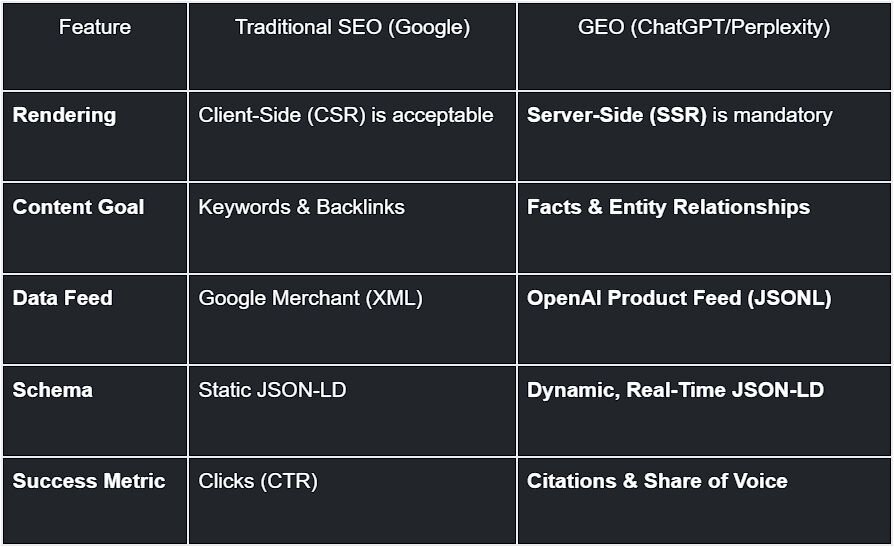
Comparison: Traditional SEO vs. Headless GEO Architecture
The requirements for ranking in an LLM differ vastly from ranking in Google. We use Builder.io to structure data for the latter column.
How does Builder.io enforce the "Inverted Pyramid" for AI?
LLMs process information top-down and prioritize content that is easy to summarize. We configure Builder.io models to enforce an "Inverted Pyramid" structure, where the most critical "answer" appears in the first 60 words.
We do not use generic text blobs. Instead, we create custom fields in Builder.io for:
1. Direct Answer Summaries: A specific field that outputs a definition or summary at the very top of the DOM.
2. Structured Specs: Using Builder's Repeater Fields to generate HTML tables for product specifications. Research shows that LLMs are significantly more likely to cite data presented in structured tables compared to unstructured text.
3. Entity Linking: We use Builder's reference fields to link products to related "Concept" pages (e.g., linking a "Camera" product to a "Photography Guide"), creating a semantic graph that helps the AI reason about utility.
What defines the OpenAI Product Feed specification?
Optimizing for "Agentic Commerce"—where AI agents execute purchases for users—requires a new data standard. Unlike Google Shopping feeds which optimize for keywords, the OpenAI Product Feed optimizes for reasoning.
We generate these feeds (in .jsonl format) via Vercel Cron Jobs that query our commerce backend (e.g., MedusaJS). Key differences include:
• Reasoning Attributes: We populate fields like pattern, material, and relationship_type (e.g., compatible_with) to help the AI answer questions like "Will this lens fit my camera?".
• Freshness: The OpenAI spec supports updates every 15 minutes. We use ISR to ensure the feed reflects real-time inventory, preventing the AI from recommending out-of-stock items.
• Checkout Flags: We explicitly set is_eligible_checkout to true, enabling the "Instant Checkout" capability directly within the chat interface.
Technical Takeaway
Transitioning to GEO is not a marketing task; it is an engineering mandate. You must move from serving static brochures to serving reasoning inputs. By combining Vercel’s SSR capabilities with Builder.io’s structured content modeling, you provide the verifiable ground truth that Generative Engines require.
Research indicates that implementing these content enrichment tactics—such as adding citations, statistics, and authoritative formatting—can boost visibility in Generative Engine responses by up to 40%.
At Seeed.us, we execute this architecture to future-proof mid-market digital platforms. If your site is invisible to AI, your customers are already talking to your competitors.
Be the first to know!
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay in the loop of technological advances that can help your business grow.